SoftBank and Asian chip stocks fall as Nvidia’s selloff ripples through global semiconductor sector
News Summary
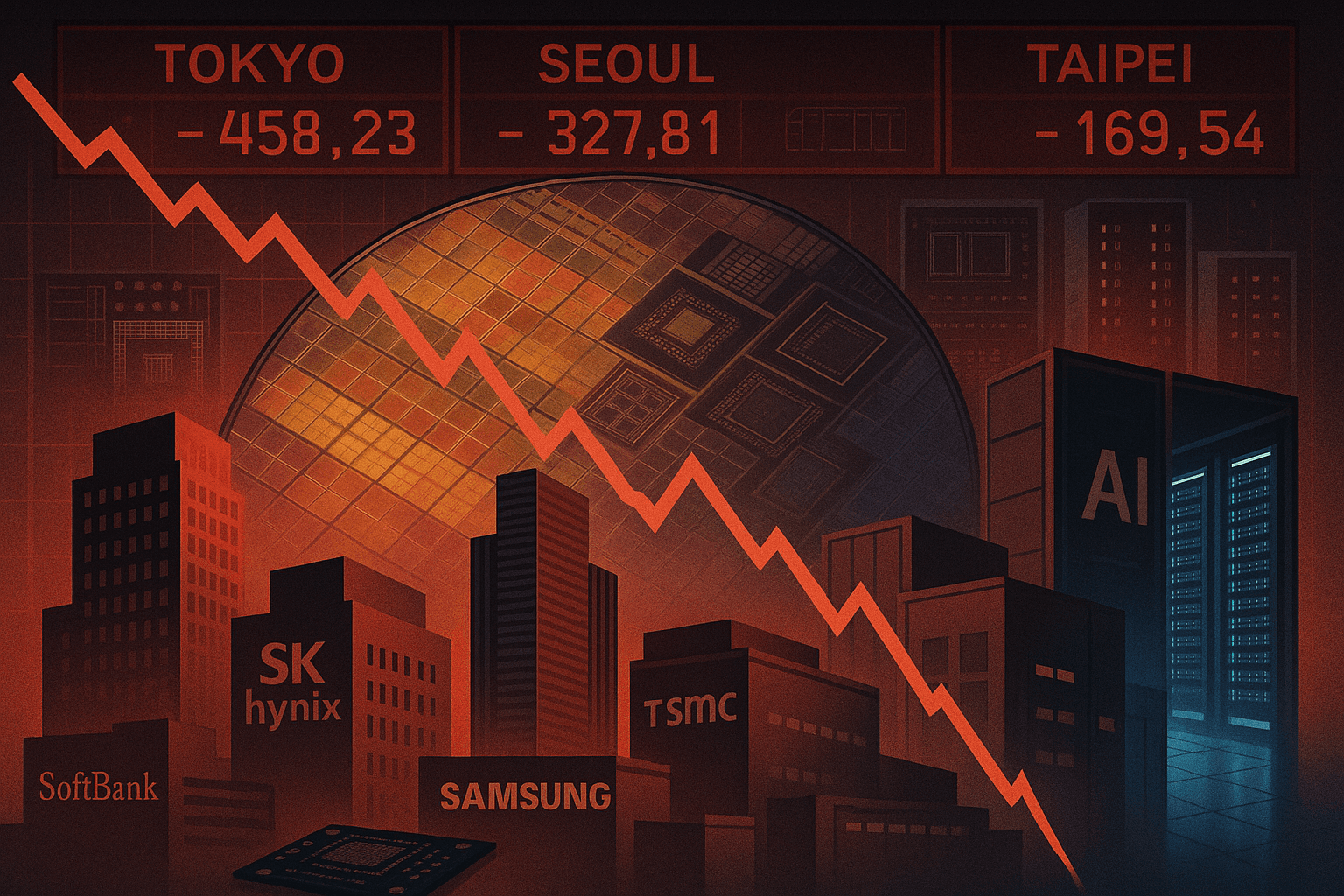
Asian chipmakers experienced sharp declines on Friday after an unexpected drop in Nvidia's stock on Wall Street, despite the US chip designer posting stronger-than-expected earnings and upbeat guidance, triggering a broad sector-wide pullback. Japan's SoftBank led the retreat, falling over 10%, following its announcement of deepening US AI data-center investments tied to OpenAI's Stargate project. The selloff impacted major chip names across Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, including SK Hynix (down 8%), Samsung Electronics (down over 5%), TSMC (down over 4%), and Foxconn (down 4%). SoftBank plans to invest up to $3 billion to convert an electric vehicle plant in Lordstown, Ohio, into a facility producing equipment for OpenAI's next-generation data centers. This investment is part of the $500 billion Stargate initiative, a broader joint venture with OpenAI and Oracle announced at the White House, to which SoftBank committed $18 billion. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman noted that their ambitious target of 30 gigawatts of computing capacity is estimated to cost $1.4 trillion, with current costs exceeding $40 billion per gigawatt, highlighting the substantial financial challenge and OpenAI's dependence on partners like SoftBank.
Background
Nvidia is a global leader in AI chip design, with its high-performance GPUs dominating the AI computing sector. SoftBank Group is a Japanese technology investment conglomerate known for its investments in global tech companies and controls British chip designer Arm, which provides core architecture for Nvidia processors. OpenAI is a leading US-based AI research and deployment company known for its large language models and AI innovations. Its "Stargate" project is an ambitious initiative to build massive AI data center infrastructure. SoftBank previously sold its $5.8 billion stake in Nvidia to finance its AI investment strategy centered on OpenAI and purchased the Lordstown facility for $375 million in August 2024.
In-Depth AI Insights
What dynamics does Nvidia's stock drop, despite strong earnings and guidance, signal for the AI hardware market? - Nvidia's decline may reflect a market adjustment to potentially stretched AI chip valuations rather than a fundamental questioning of its performance. After a prolonged period of explosive growth, some investors may be taking profits or re-evaluating the sustainability of AI hardware demand growth. - This could also indicate that the market is beginning to factor in the capital intensiveness and inherent volatility of AI infrastructure buildouts. While long-term demand remains optimistic, short-term uncertainties around supply chains, technological iterations, and macroeconomics might lead to increased investor caution. - Furthermore, as a market bellwether, Nvidia's pullback could signal greater near-term pressure and valuation reassessments across the broader semiconductor sector, particularly for major Asian foundry and memory chip suppliers. What are the deeper strategic considerations and potential risks behind the massive collaboration between SoftBank, OpenAI, and Oracle? - SoftBank's substantial investment in the Stargate project aims to secure core benefits from the "picks and shovels" role of AI infrastructure by deeply tying itself to OpenAI, a leader in AI content and models, rather than merely holding chip stocks. This represents a more controlled strategic pivot. The announcement of the collaboration at the White House with the Trump administration also underscores national-level support, potentially aligning with US strategic positioning for AI technological dominance. - However, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman's emphasis on the colossal $1.4 trillion funding requirement and current high costs per gigawatt highlights the extreme capital intensity of the Stargate project. OpenAI's lack of a large advertising or cloud business to subsidize these investments makes it highly dependent on external financing and partners, introducing significant execution and financial risks for SoftBank and Oracle. - This deep entanglement also means that if OpenAI faces setbacks in its technological roadmap, model commercialization, or profitability, SoftBank's investment will be exposed to direct and substantial risk. The project's long-term success hinges not only on technological breakthroughs but also on the effective management of such massive and continuously growing capital expenditures. Considering the immense capital requirements for AI infrastructure and OpenAI's business model, how should investors evaluate the long-term prospects of the AI chip and related infrastructure sectors? - The ultra-large-scale investment required for AI infrastructure, such as OpenAI's 30 gigawatt computing capacity target, implies strong and sustained demand for AI chips (GPUs), high-speed interconnects, advanced memory, and data center equipment over the next decade. This represents a long-term tailwind for core suppliers like Nvidia, TSMC, and SK Hynix. - However, this growth is not without challenges. High capital expenditures could lead to extended project timelines, funding strains, and may prompt AI giants to seek more cost-effective solutions, such as in-house chip development or optimizing existing architectures, thereby increasing competitive pressure on upstream suppliers. - Investors need to carefully differentiate the risks and rewards within the value chain for "water sellers" (e.g., data center operators, power providers) versus "shovel sellers" (e.g., chip manufacturers). The buildout of AI infrastructure is a long game, and profitability models and return on investment may take longer to materialize, requiring investors to have long-term patience and tolerance for volatility.